A collection of pre-defined HRF objects for common fMRI analysis scenarios. These objects can be used directly in model specifications or as templates for creating custom HRFs.
Value
When called as functions, return numeric vectors or matrices of HRF values.
When used as objects, they are HRF objects with class c("HRF", "function").
Canonical HRFs
HRF_SPMG1SPM canonical HRF (single basis function)
HRF_SPMG2SPM canonical HRF with temporal derivative (2 basis functions)
HRF_SPMG3SPM canonical HRF with temporal and dispersion derivatives (3 basis functions)
HRF_GAMMAGamma function-based HRF
HRF_GAUSSIANGaussian function-based HRF
Flexible Basis Sets
HRF_BSPLINEB-spline basis HRF (5 basis functions)
HRF_FIRFinite Impulse Response (FIR) basis HRF (12 basis functions)
Creating Custom Basis Sets
The pre-defined objects above have fixed numbers of basis functions. To create basis sets with custom parameters (e.g., different numbers of basis functions), use one of these approaches:
Using getHRF():
getHRF("fir", nbasis = 20)- FIR basis with 20 functionsgetHRF("bspline", nbasis = 10, span = 30)- B-spline with 10 functionsgetHRF("fourier", nbasis = 7)- Fourier basis with 7 functionsgetHRF("daguerre", nbasis = 5, scale = 3)- Daguerre basis
Using generator functions directly:
hrf_fir_generator(nbasis = 20, span = 30)hrf_bspline_generator(nbasis = 10, span = 30)hrf_fourier_generator(nbasis = 7, span = 24)hrf_daguerre_generator(nbasis = 5, scale = 3)
Usage
All HRF objects can be:
Called as functions with time argument:
HRF_SPMG1(t)Used in model specifications:
hrf(condition, basis = HRF_SPMG1)Evaluated with
evaluate()methodCombined with decorators like
lag_hrf()orblock_hrf()
See also
evaluate.HRF for evaluating HRF objects,
gen_hrf for creating HRFs with decorators,
list_available_hrfs for listing all HRF types,
getHRF for creating HRFs by name with custom parameters,
hrf_fir_generator, hrf_bspline_generator,
hrf_fourier_generator, hrf_daguerre_generator
for creating custom basis sets directly
Other hrf:
deriv(),
penalty_matrix()
Examples
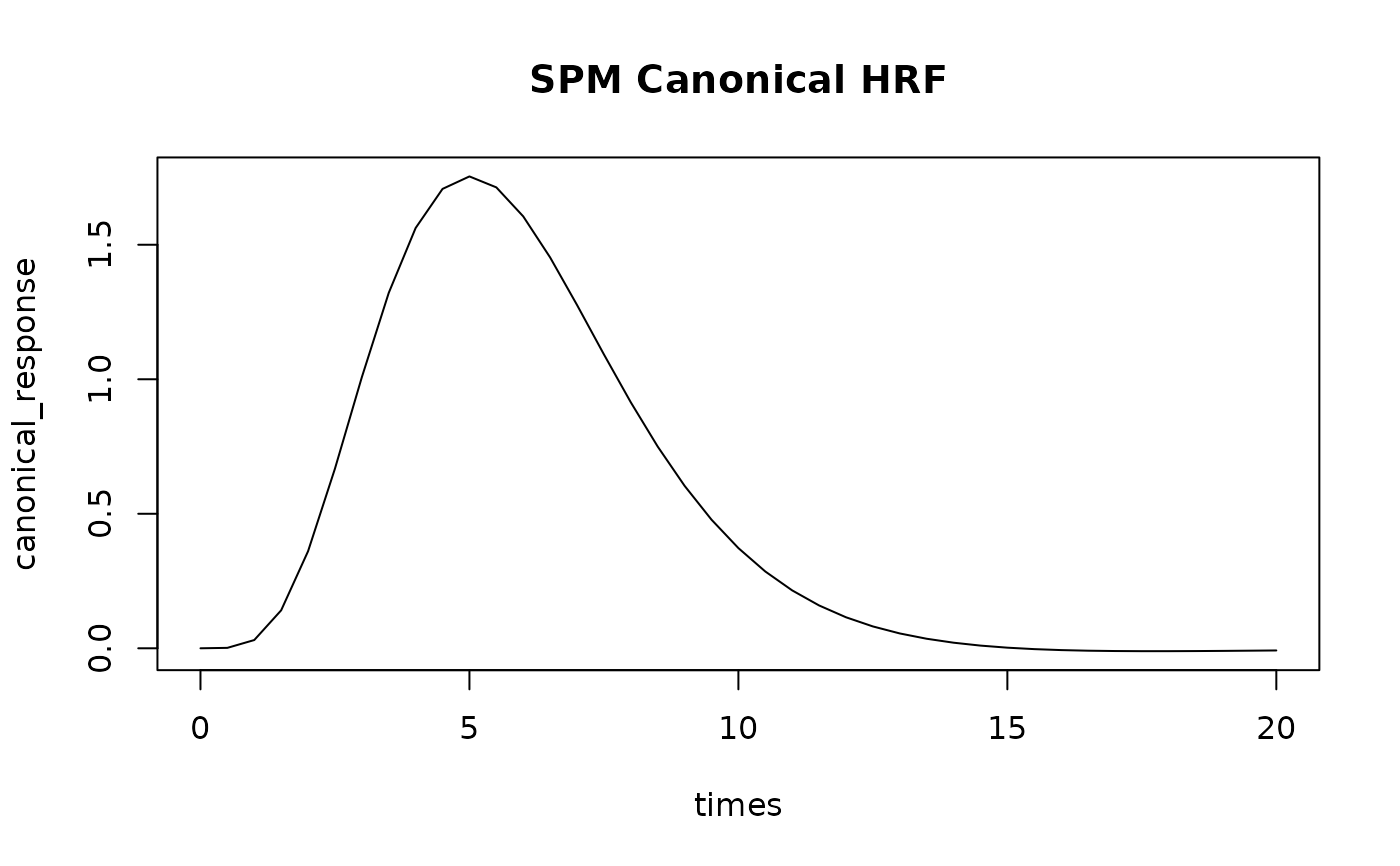
# Evaluate HRFs at specific time points
times <- seq(0, 20, by = 0.5)
# Single basis canonical HRF
canonical_response <- HRF_SPMG1(times)
plot(times, canonical_response, type = "l", main = "SPM Canonical HRF")
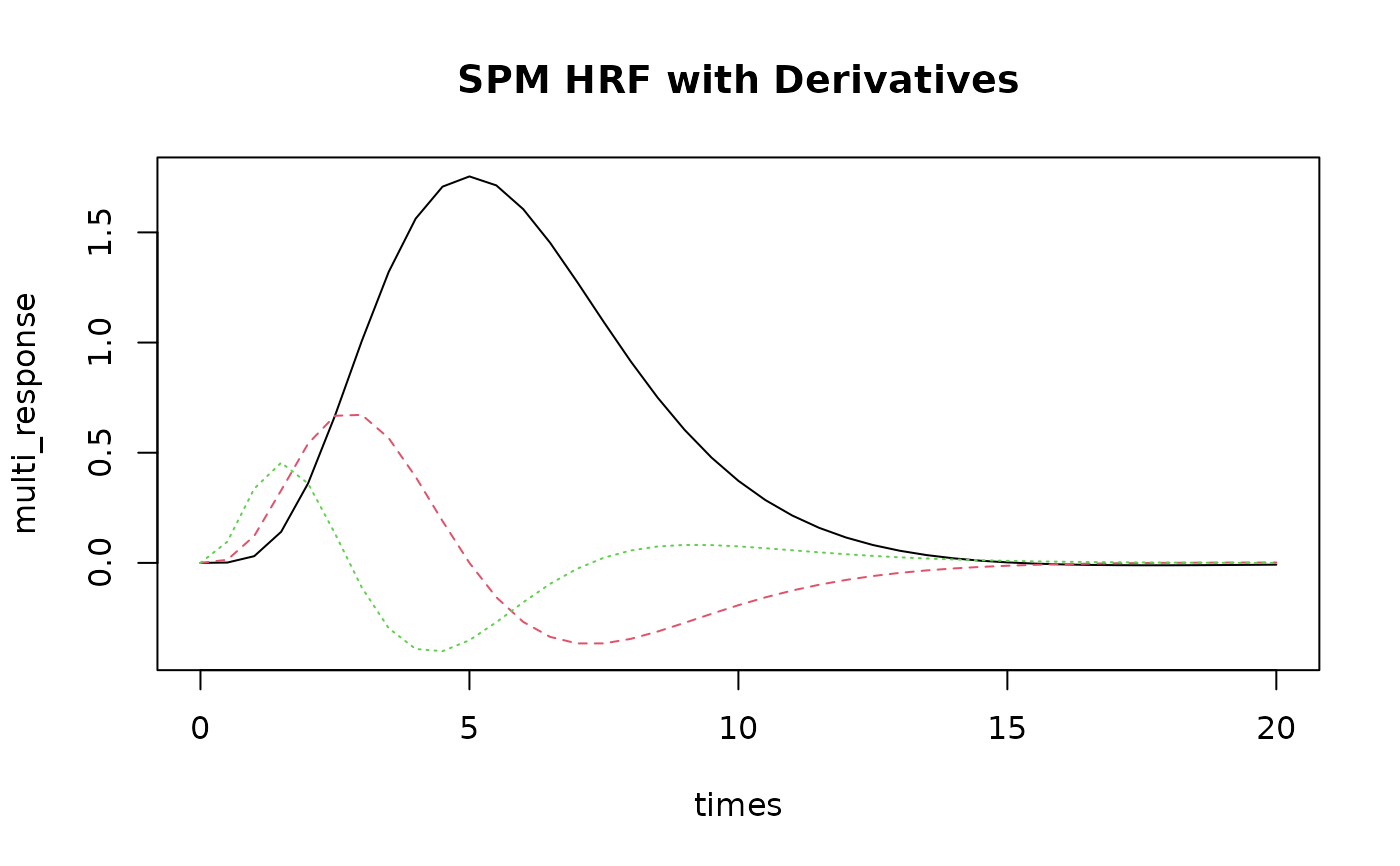
 # Multi-basis HRF with derivatives
multi_response <- HRF_SPMG3(times) # Returns 3-column matrix
matplot(times, multi_response, type = "l", main = "SPM HRF with Derivatives")
# Multi-basis HRF with derivatives
multi_response <- HRF_SPMG3(times) # Returns 3-column matrix
matplot(times, multi_response, type = "l", main = "SPM HRF with Derivatives")
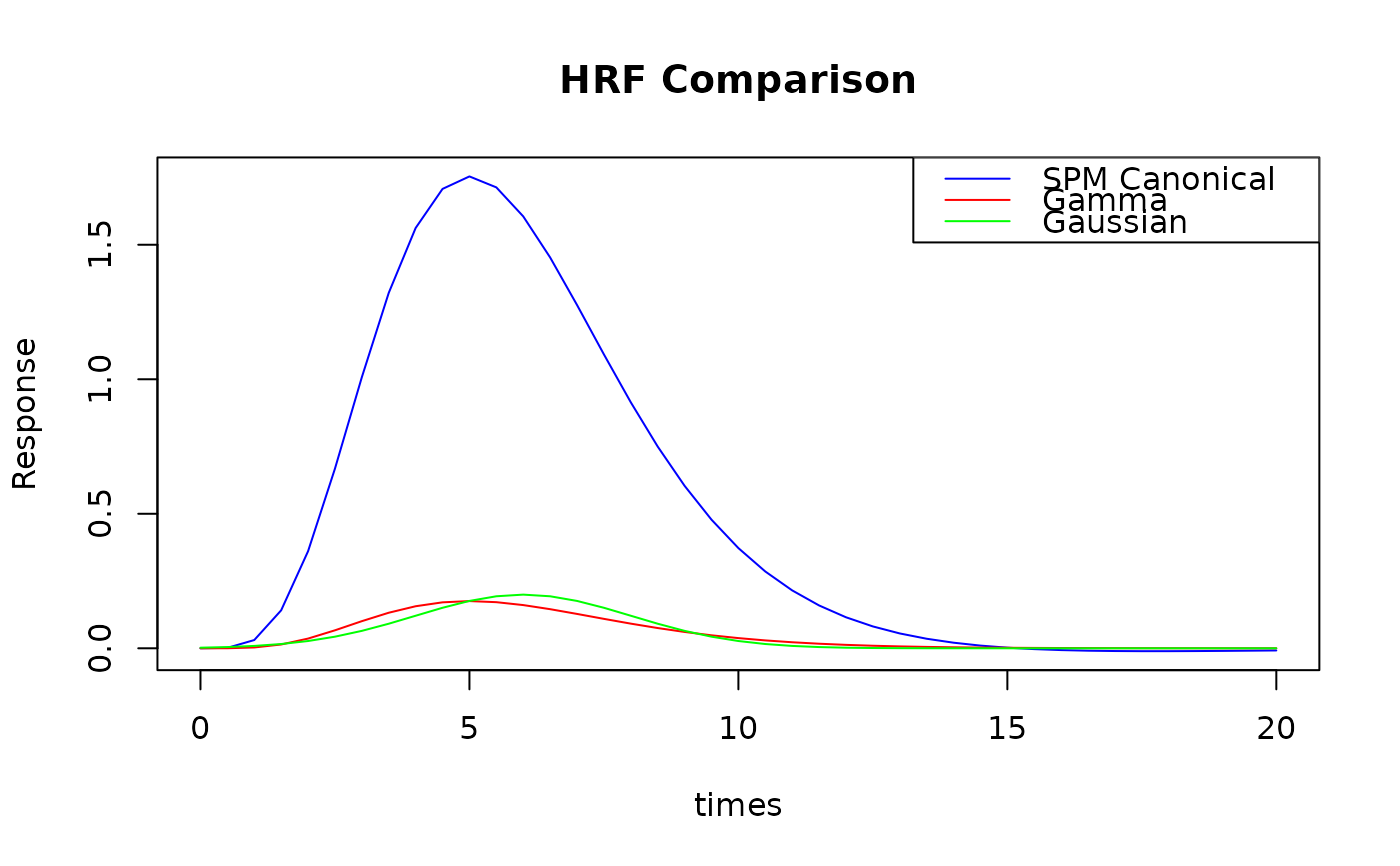
 # Gamma and Gaussian HRFs
gamma_response <- HRF_GAMMA(times)
gaussian_response <- HRF_GAUSSIAN(times)
# Compare different HRF shapes
plot(times, canonical_response, type = "l", col = "blue",
main = "HRF Comparison", ylab = "Response")
lines(times, gamma_response, col = "red")
lines(times, gaussian_response, col = "green")
legend("topright", c("SPM Canonical", "Gamma", "Gaussian"),
col = c("blue", "red", "green"), lty = 1)
# Gamma and Gaussian HRFs
gamma_response <- HRF_GAMMA(times)
gaussian_response <- HRF_GAUSSIAN(times)
# Compare different HRF shapes
plot(times, canonical_response, type = "l", col = "blue",
main = "HRF Comparison", ylab = "Response")
lines(times, gamma_response, col = "red")
lines(times, gaussian_response, col = "green")
legend("topright", c("SPM Canonical", "Gamma", "Gaussian"),
col = c("blue", "red", "green"), lty = 1)
 # Create custom FIR basis with 20 bins
custom_fir <- getHRF("fir", nbasis = 20, span = 30)
fir_response <- evaluate(custom_fir, times)
matplot(times, fir_response, type = "l", main = "Custom FIR with 20 bins")
# Create custom FIR basis with 20 bins
custom_fir <- getHRF("fir", nbasis = 20, span = 30)
fir_response <- evaluate(custom_fir, times)
matplot(times, fir_response, type = "l", main = "Custom FIR with 20 bins")
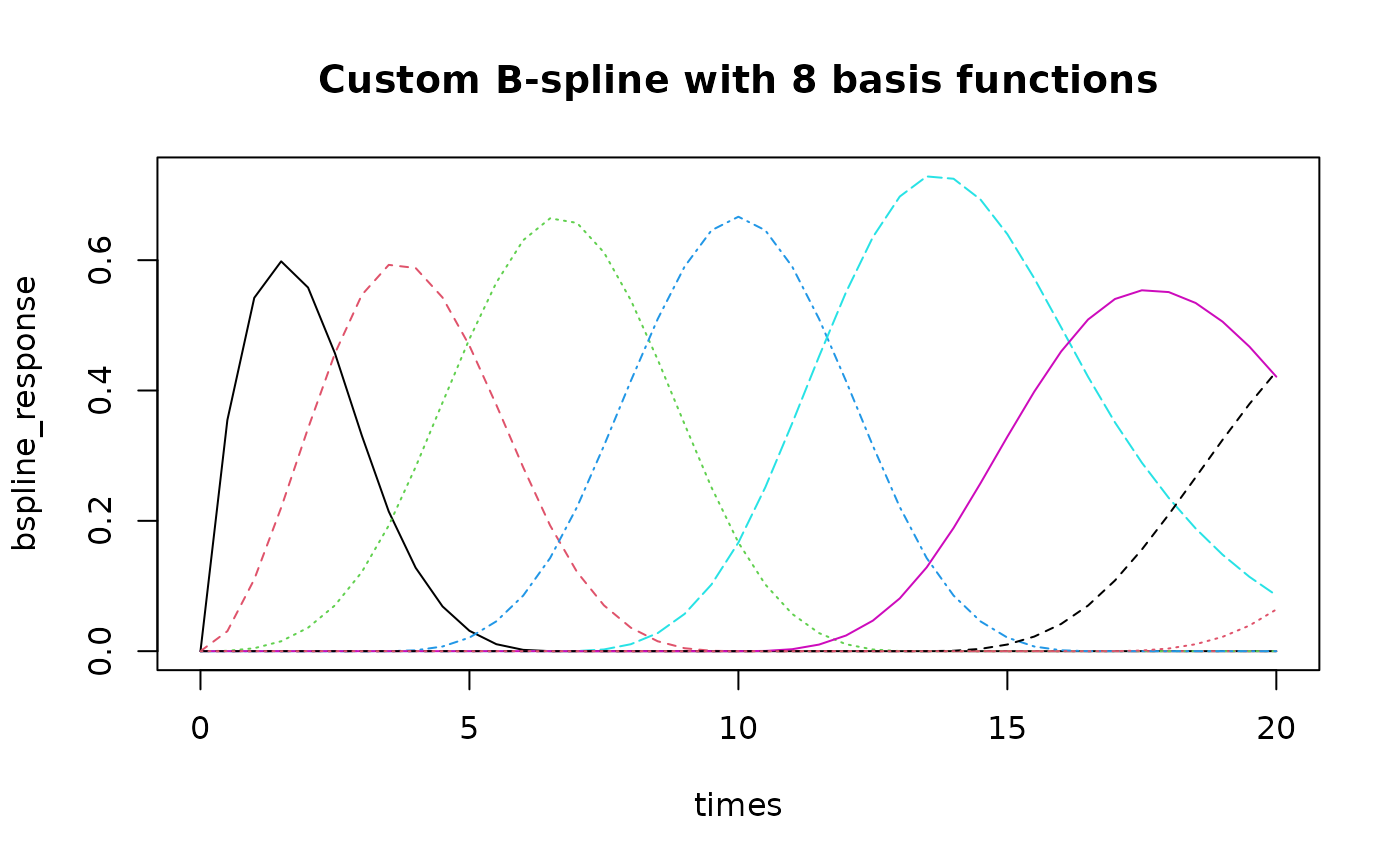
 # Create custom B-spline basis
custom_bspline <- hrf_bspline_generator(nbasis = 8, span = 25)
bspline_response <- evaluate(custom_bspline, times)
matplot(times, bspline_response, type = "l", main = "Custom B-spline with 8 basis functions")
# Create custom B-spline basis
custom_bspline <- hrf_bspline_generator(nbasis = 8, span = 25)
bspline_response <- evaluate(custom_bspline, times)
matplot(times, bspline_response, type = "l", main = "Custom B-spline with 8 basis functions")